

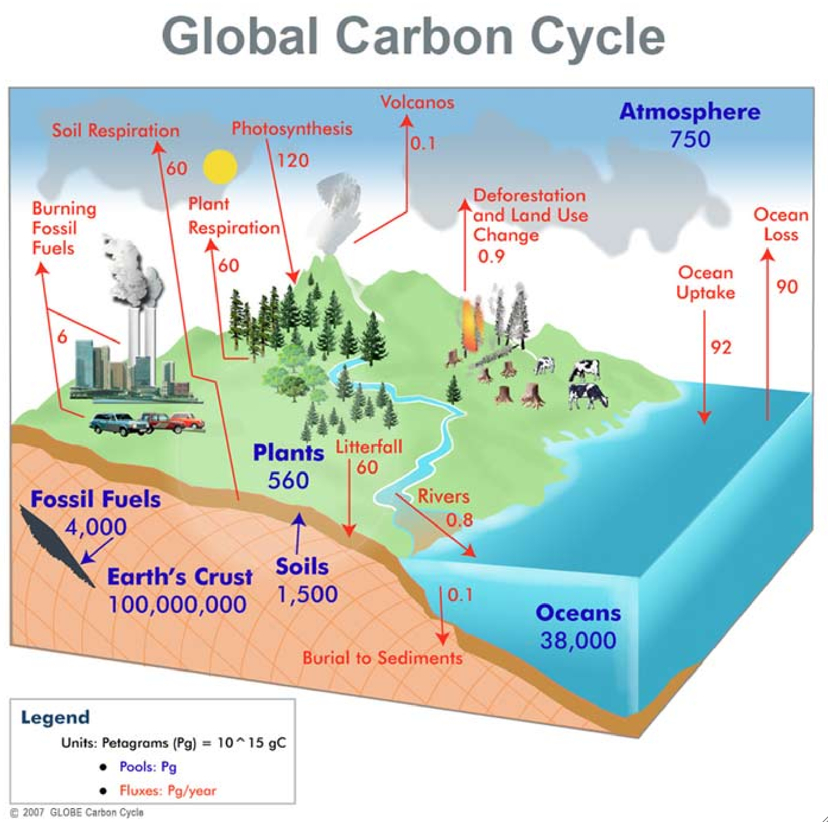
Bacterial action in decomposition releases CO2 back to the atmosphere. Carbon is transferred to the soil via leaf litter, roots and plant debris upon decomposition. Carbon is stored within biomass, such as tropical and temperate forests. This sequence proceeds as follows: A carbon-12 nucleus captures a proton and emits a gamma ray, producing nitrogen-13. The carbon cycle on land (terrestrial) Dominated by photosynthesis of plants absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere. Ocean-atmosphere exchange: there is a mutual transfer of CO 2 between the lower atmosphere and ocean surfaces. The ‘ CNO cycle’ refers to the Carbon-Nitrogen-Oxygen cycle, a process of stellar nucleosynthesis in which stars on the Main Sequence fuse hydrogen into helium via a six-stage sequence of reactions.Combustion: natural fires release carbon compounds from vegetation to the atmosphereĪll these involve living (organic) processes in some way.Īdditionally, there is an on-going transfer of CO 2 that is non-organic:.Where oxygen is present it releases CO 2, where it is absent CH 4 is released. Decomposition: the breakdown of animals and plant structures by bacteria and the release of carbon compounds into the atmosphere, soil and to the ocean floor.
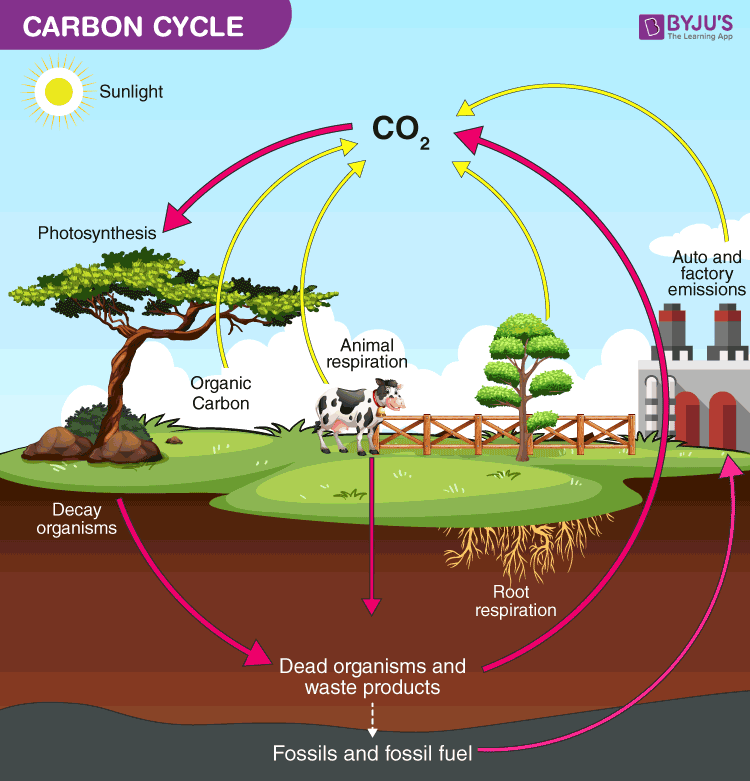
Digestion: the release of carbon compounds by terrestrial and marine animals after feeding on carbon-rich material. To prepare a model of carbon footprint assessment of the system of wastewater collection, transport and treatment, an original method consisting of five stages was employed, these being: preparing.Respiration: the release of CO2 into the atmosphere, soil and oceans by animals as they exhale.Photosynthesis: the absorption of CO 2 from the atmosphere (terrestrial plants) and from oceans (marine plants) to produce organic carbon structures.This report will give a brief description of the main stages in this cycle. The key processes in the fast carbon cycle include: The diagram shows how carbon moves through various stages to form a complete cycle. RuBP has five atoms of carbon and a phosphate group on each end. The TCA cycle (which is also known as the Krebs, or citric acid, cycle) plays a central role in the breakdown, or catabolism, of organic fuel molecules.The cycle is made up of eight steps catalyzed by eight different enzymes that produce energy at several different stages. In the stroma, in addition to CO 2, two other chemicals are present to initiate the Calvin cycle: an enzyme abbreviated RuBisCO, and the molecule ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). A simple carbon cycle without interference from human activity includes the following stages: plants and animals emit CO2 during respiration, photosynthetic plants use CO2 in photosynthesis, organisms give off CO2 when they decompose, and carbon is stored fossil fuels and sediments for long periods of time before processes such as erosion and. The fast carbon cycle operates on a daily basis as living things breathe and digest food and influencing changes to carbon stores over decades and centuries. 2) can be organized into three basic stages: fixation, reduction, and regeneration.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
